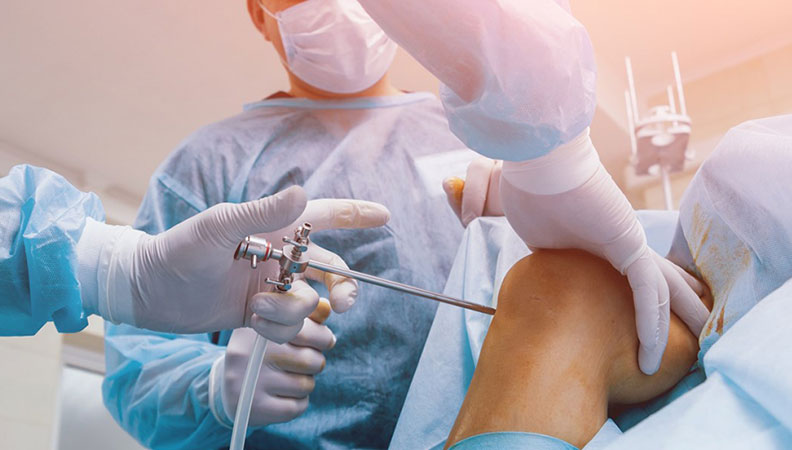
Orthopaedics: A Comprehensive Overview
Orthopaedics is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and rehabilitation of disorders and injuries of the musculoskeletal system. This system includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves, all of which work together to allow movement and provide structural support to the body. Orthopaedic specialists, known as orthopaedic surgeons or orthopaedists, play a critical role in treating a wide range of conditions, from fractures to chronic diseases such as arthritis.
Common Orthopaedic Conditions
Orthopaedic issues can affect people of all ages and vary in severity. Some common conditions include:
Fractures: Broken bones caused by trauma or accidents are among the most frequently treated injuries in orthopaedics. Treatment typically involves immobilization with casts or surgical fixation using plates and screws.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two common types of arthritis that affect the joints. These conditions cause inflammation, pain, and reduced mobility.
Sports injuries: Athletes frequently experience injuries such as ligament tears (e.g., ACL tears), sprains, and tendonitis, all of which require specialized treatment to restore function and prevent further damage.
Spinal disorders: Back pain, scoliosis, and herniated discs are some of the common spinal problems addressed by orthopaedic surgeons. Treatments range from physical therapy to complex surgical procedures like spinal fusion.
Treatment Methods
Orthopaedics employs both surgical and non-surgical treatments depending on the condition. Non-surgical treatments include:
Physical therapy: A key component in the recovery process, physical therapy helps strengthen muscles and improve mobility, especially after injuries or surgeries.
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and injections (e.g., cortisone) are commonly used to manage symptoms like pain and inflammation.
Bracing and supports: These devices help immobilize affected areas, allowing for healing and reducing the risk of further injury.
When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary. Some common orthopaedic surgeries include:
Joint replacement: Procedures like total knee or hip replacement are performed when joints are severely damaged by arthritis or injury.
Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery used to diagnose and treat joint problems, such as torn cartilage or damaged ligaments.
Fracture repair: Surgeons often use metal rods, screws, or plates to stabilize broken bones.