Intensive Care: A Lifeline for Critical Patients
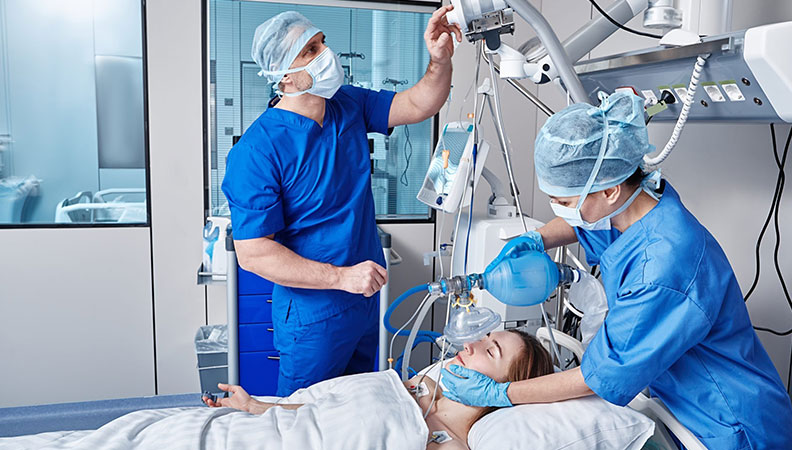
Intensive Care Units (ICUs) play a vital role in modern healthcare by providing life-saving support to patients in critical conditions. These units are specially equipped to care for those suffering from severe illnesses or injuries, requiring constant monitoring and advanced medical interventions. The ICU is staffed by highly trained professionals, including doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other specialists, who work around the clock to ensure that patients receive the necessary care.
One of the primary functions of an ICU is the use of sophisticated technology to monitor and support vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and respiratory status. This enables healthcare professionals to detect any changes in a patient’s condition promptly and take immediate action to prevent deterioration. Common equipment found in an ICU includes ventilators, infusion pumps, dialysis machines, and cardiac monitors. These machines help to sustain life when patients’ organs are unable to function independently.
Patients in ICUs often have a wide range of conditions, including trauma from accidents, severe infections like sepsis, heart attacks, stroke, or complications following major surgeries. These patients are usually in unstable conditions, requiring frequent adjustments to their treatment plans. The medical staff continuously assess these patients, administering medications, fluids, or life-support interventions as needed. The goal of ICU care is not only to stabilize the patient but also to provide the necessary interventions to promote recovery.
One of the most important aspects of intensive care is the team-based approach. ICU teams work closely to develop individualized care plans tailored to each patient's specific needs. This often includes consultations with other medical specialists and the involvement of family members in decision-making, especially when it comes to life-sustaining treatments.
The environment of an ICU can be overwhelming for both patients and their families. The constant beeping of machines, the presence of tubes, and the sight of critically ill loved ones can create a stressful atmosphere. However, the support and communication between healthcare providers and families are crucial in navigating these difficult situations.
In summary, intensive care is a critical aspect of healthcare, providing advanced support to patients in life-threatening conditions. Through the use of cutting-edge technology and a multidisciplinary team, ICUs are able to save lives and offer a path to recovery for many patients who might otherwise not survive.
Types of Intensive Care Units
General Intensive Care Unit (ICU) The general ICU is equipped to handle a broad range of critical conditions affecting multiple organ systems. Patients in these units may require intensive monitoring and support for issues such as sepsis, multi-organ failure, or severe trauma.
Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU) The CICU specializes in the care of patients with severe cardiac conditions. This includes those recovering from major heart surgeries, experiencing acute heart attacks, or suffering from severe arrhythmias. The CICU is equipped with advanced cardiac monitoring and intervention technologies.
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) The NICU provides specialized care for newborns, particularly premature infants or those with serious medical conditions. This unit focuses on managing conditions such as respiratory distress syndrome, congenital anomalies, and infections in neonates.